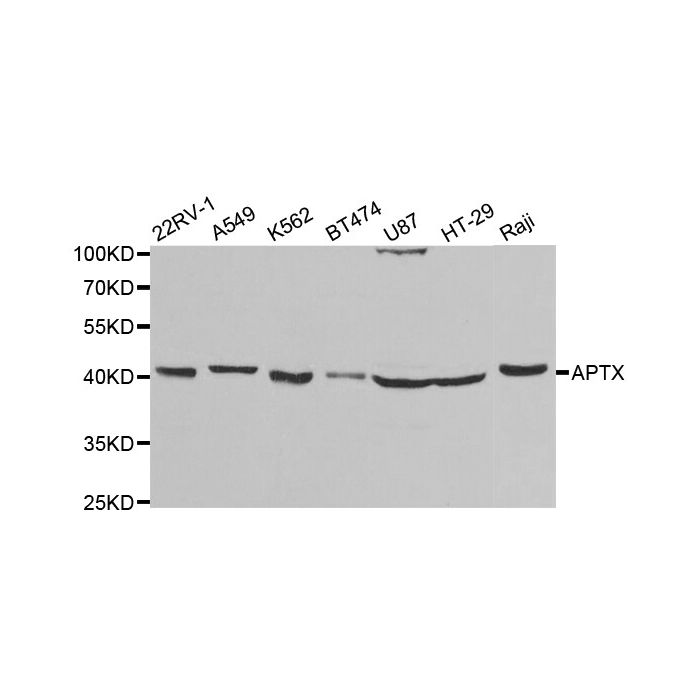
APTX polyclonal, anti-human, mouse
€388.00
In stock
SKU
BS7755
Background:
Aprataxin is a nuclear protein, present in both the nucleoplasm and the nucleolus, which is a member of the histidine triad (HIT) superfamily. Aprataxin is involved in DNA single-strand break repair, mediating protein-protein interactions with molecules responding to DNA damage. Aprataxin contains three conserved domains: an N-terminal forkhead-associated (FHA) domain which mediates protein-protein interactions, a HIT domain that is similar to Hint, and a C-terminal zinc finger domain. Loss of function mutations in APTX, the gene encoding for Aprataxin, destabilize the Aprataxin protein and result in a rare neurological disorder known as ataxia-oculomotor apraxia, characterized by abnormal movements of the head and eyes. These mutations either target the HIT domain or truncate the protein N-terminal to a zinc finger.
Alternative Name:
AOA 1, AOA, AOA1, Aprataxin, Aprataxin homolog, Aptx, APTX_HUMAN, Ataxia 1 early onset with hypoalbuminemia, Ataxia1 early onset with hypoalbuminemia, AXA 1, AXA1, EAOH, EOAHA, FHA HIT, FHA-HIT, FLJ20157, Forkhead associated domain histidine triad like, Forkhead associated domain histidine triad like protein, Forkhead-associated domain histidine triad-like protein, MGC1072,
Application Dilution: WB: 1:500 - 1:2000, IF: 1:50 - 1:100, IP: 1:20 - 1:50
Specificity: APTX polyclonal antibody detects endogenous levels of APTX protein.
Immunogen:
Recombinant full length Human APTX.
MW: ~ 41 kDa
Swis Prot.: Q7Z2E3
Purification & Purity:
The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen and the purity is > 95% (by SDS-PAGE).
Format:
1mg/ml in PBS with 0.1% Sodium Azide, 50% Glycerol.
Storage:
Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles.
For research use only, not for use in diagnostic procedure.
Aprataxin is a nuclear protein, present in both the nucleoplasm and the nucleolus, which is a member of the histidine triad (HIT) superfamily. Aprataxin is involved in DNA single-strand break repair, mediating protein-protein interactions with molecules responding to DNA damage. Aprataxin contains three conserved domains: an N-terminal forkhead-associated (FHA) domain which mediates protein-protein interactions, a HIT domain that is similar to Hint, and a C-terminal zinc finger domain. Loss of function mutations in APTX, the gene encoding for Aprataxin, destabilize the Aprataxin protein and result in a rare neurological disorder known as ataxia-oculomotor apraxia, characterized by abnormal movements of the head and eyes. These mutations either target the HIT domain or truncate the protein N-terminal to a zinc finger.
Alternative Name:
AOA 1, AOA, AOA1, Aprataxin, Aprataxin homolog, Aptx, APTX_HUMAN, Ataxia 1 early onset with hypoalbuminemia, Ataxia1 early onset with hypoalbuminemia, AXA 1, AXA1, EAOH, EOAHA, FHA HIT, FHA-HIT, FLJ20157, Forkhead associated domain histidine triad like, Forkhead associated domain histidine triad like protein, Forkhead-associated domain histidine triad-like protein, MGC1072,
Application Dilution: WB: 1:500 - 1:2000, IF: 1:50 - 1:100, IP: 1:20 - 1:50
Specificity: APTX polyclonal antibody detects endogenous levels of APTX protein.
Immunogen:
Recombinant full length Human APTX.
MW: ~ 41 kDa
Swis Prot.: Q7Z2E3
Purification & Purity:
The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen and the purity is > 95% (by SDS-PAGE).
Format:
1mg/ml in PBS with 0.1% Sodium Azide, 50% Glycerol.
Storage:
Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles.
For research use only, not for use in diagnostic procedure.
| Is Featured? | No |
|---|
Write Your Own Review