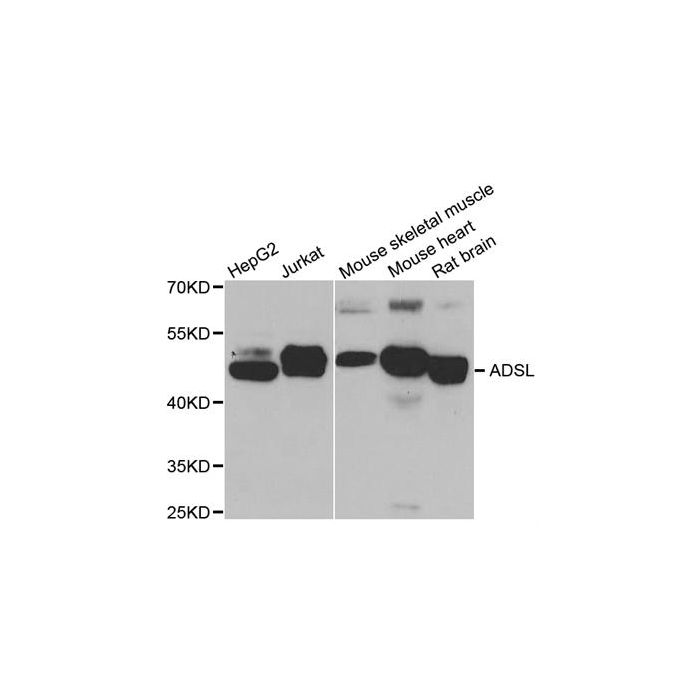
ADSL polyclonal, anti-human, mouse, rat
€388.00
In stock
SKU
BS8096
Background:
ADSL (adenylosuccinate lyase), also known as AMPS, ASL or ASASE, is a 484 amino acid protein that is involved in both purine biosynthesis and in the formation of adenosine monophosphate (AMP) from inosine monophosphate. Expressed ubiquitously, ADSL catalyzes two key reactions in AMP biosynthesis, namely the removal of a fumarate from succinylaminoimidazole carboxamide (SAICA) ribotide to give aminoimidazole carboxamide ribotide (AICA) and the subsequent removal of fumarate from adenylosuccinate to yield AMP. Defects in the gene encoding ADSL are the cause of adenylosuccinase deficiency (ADSL deficiency), an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by epilepsy, growth retardation and muscular wasting. Multiple isoforms of ADSL exist due to alternative splicing events.
Alternative Name:
Adenylosuccinate lyase, ASL, Adenylosuccinase, Asase, ADSL, AMPS
Application Dilution: WB: 1:500~1:2000, IF: 1:20~1:100, IP: 1:50 - 1:100
Specificity: ADSL polyclonal antibody detects endogenous levels of ADSL protein.
Immunogen:
Recombinant full length Human ADSL.
MW: ~ 55 kDa
Swis Prot.: P30566
Purification & Purity:
The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen and the purity is > 95% (by SDS-PAGE).
Format:
1mg/ml in PBS with 0.1% Sodium Azide, 50% Glycerol.
Storage:
Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles.
For research use only, not for use in diagnostic procedure.
ADSL (adenylosuccinate lyase), also known as AMPS, ASL or ASASE, is a 484 amino acid protein that is involved in both purine biosynthesis and in the formation of adenosine monophosphate (AMP) from inosine monophosphate. Expressed ubiquitously, ADSL catalyzes two key reactions in AMP biosynthesis, namely the removal of a fumarate from succinylaminoimidazole carboxamide (SAICA) ribotide to give aminoimidazole carboxamide ribotide (AICA) and the subsequent removal of fumarate from adenylosuccinate to yield AMP. Defects in the gene encoding ADSL are the cause of adenylosuccinase deficiency (ADSL deficiency), an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by epilepsy, growth retardation and muscular wasting. Multiple isoforms of ADSL exist due to alternative splicing events.
Alternative Name:
Adenylosuccinate lyase, ASL, Adenylosuccinase, Asase, ADSL, AMPS
Application Dilution: WB: 1:500~1:2000, IF: 1:20~1:100, IP: 1:50 - 1:100
Specificity: ADSL polyclonal antibody detects endogenous levels of ADSL protein.
Immunogen:
Recombinant full length Human ADSL.
MW: ~ 55 kDa
Swis Prot.: P30566
Purification & Purity:
The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen and the purity is > 95% (by SDS-PAGE).
Format:
1mg/ml in PBS with 0.1% Sodium Azide, 50% Glycerol.
Storage:
Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles.
For research use only, not for use in diagnostic procedure.
| Is Featured? | No |
|---|
Write Your Own Review