AICDA polyclonal, anti-human, mouse, rat
€305.00
In stock
SKU
BS60546
Background:
Activation-induced Cytidine Deaminase (AID, HIGM-2) is a 198-amino acid, RNA-editing enzyme that contains a conserved cytidine deaminase motif and plays an important role in B-cell terminal differentiation. AID is expressed in germinal center B cells and contributes to the production of neutralizing antibodies IgG, IgA, and IgE. Hyper-IgM syndrome (HIGM2) patients that have deficient levels of AID show the absence of immuno-globulin class switch recombination (CSR), lack of immuno-globulin somatic hypermutations, and lymph node hyperplasia mediated by the presence of giant germinal centers. Furthermore, AID-/- mice are defective in CSR and also show a hyper-IgM phenotype, characterized by enlarged germinal centers containing active B cells. AID thus appears to be required in several stages of B-cell terminal differentiation that are necessary for efficient antibody responses such as B cell proliferation, immunoglobulin somatic hypermutations and CSR.
Alternative Name:
Single-stranded DNA cytosine deaminase, Activation-induced cytidine deaminase, Cytidine aminohydrolase, AICDA, AID
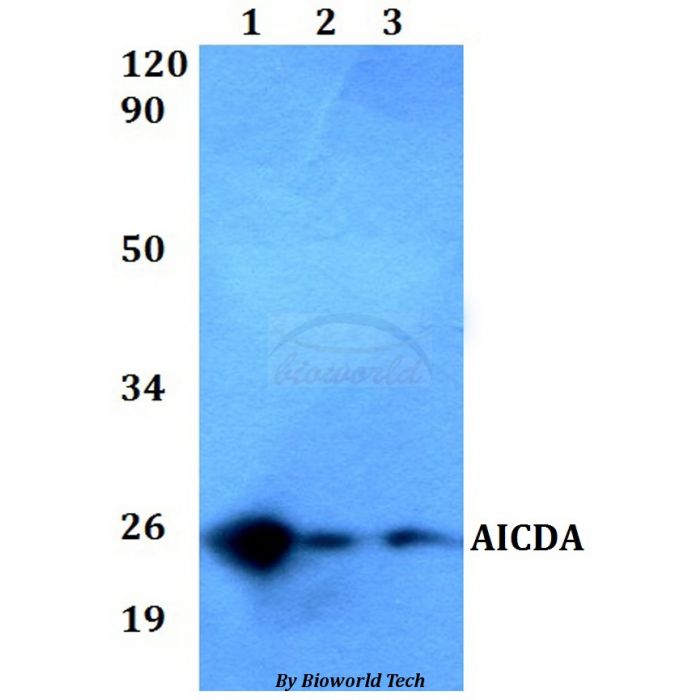
Application Dilution: WB: 1:500~1:1000
Specificity: AICDA polyclonal antibody detects endogenous levels of AICDA protein.
Immunogen:
A synthetic peptide corresponding to residues in Human AICDA
MW: ~ 24 kDa
Swis Prot.: Q9GZX7
Purification & Purity:
The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen and the purity is > 95% (by SDS-PAGE).
Format:
1 mg/ml in Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) with 15 mM sodium azide, approx. pH 7.2.
Storage:
Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles.
For research use only, not for use in diagnostic procedure.
Activation-induced Cytidine Deaminase (AID, HIGM-2) is a 198-amino acid, RNA-editing enzyme that contains a conserved cytidine deaminase motif and plays an important role in B-cell terminal differentiation. AID is expressed in germinal center B cells and contributes to the production of neutralizing antibodies IgG, IgA, and IgE. Hyper-IgM syndrome (HIGM2) patients that have deficient levels of AID show the absence of immuno-globulin class switch recombination (CSR), lack of immuno-globulin somatic hypermutations, and lymph node hyperplasia mediated by the presence of giant germinal centers. Furthermore, AID-/- mice are defective in CSR and also show a hyper-IgM phenotype, characterized by enlarged germinal centers containing active B cells. AID thus appears to be required in several stages of B-cell terminal differentiation that are necessary for efficient antibody responses such as B cell proliferation, immunoglobulin somatic hypermutations and CSR.
Alternative Name:
Single-stranded DNA cytosine deaminase, Activation-induced cytidine deaminase, Cytidine aminohydrolase, AICDA, AID
Application Dilution: WB: 1:500~1:1000
Specificity: AICDA polyclonal antibody detects endogenous levels of AICDA protein.
Immunogen:
A synthetic peptide corresponding to residues in Human AICDA
MW: ~ 24 kDa
Swis Prot.: Q9GZX7
Purification & Purity:
The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen and the purity is > 95% (by SDS-PAGE).
Format:
1 mg/ml in Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) with 15 mM sodium azide, approx. pH 7.2.
Storage:
Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles.
For research use only, not for use in diagnostic procedure.
| Is Featured? | No |
|---|
Write Your Own Review