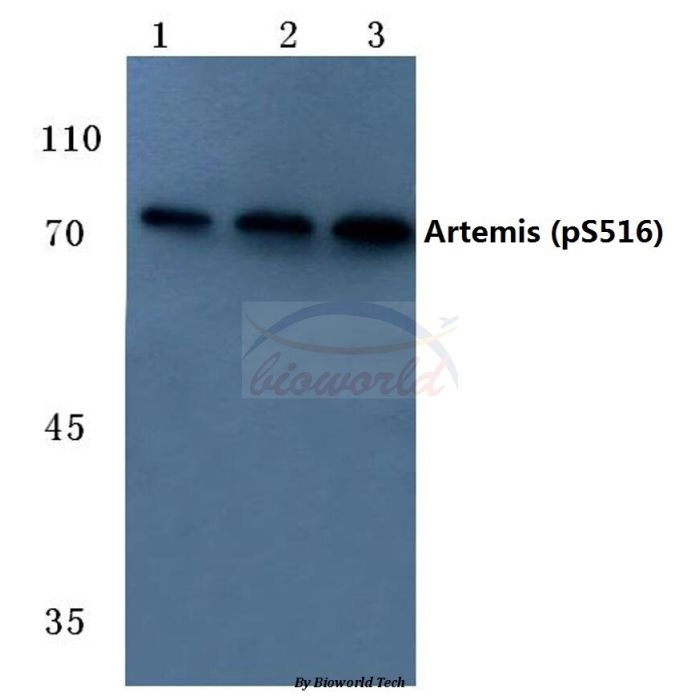
Artemis (phospho-S516) polyclonal, anti-human, mouse, rat
€328.00
In stock
SKU
BS4644
Background:
Distinct DNA repair pathways minimize the consequences of mutagenic events. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are highly reactive atoms with an unpaired electron that are conducive to double-strand DNA breaking events. Artemis, named after the Greek goddess for the protection of children, is one of the major proteins contributing to the preservation of double-strand breaks in DNA by cutting away the damaged parts of the DNA, which allows the strands to rejoin. Artemis is a single-strand-specific 5' to 3' exonuclease that forms a complex with the 469 kDa DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PKcs). DNA-PKcs phosphorylates Artemis, and Artemis acquires endonucleolytic activity on 5' and 3' overhangs and hairpins. These activities are essential for V(D)J recombination and for the 5' and 3' overhang processing in nonhomologous DNA end joining.
Alternative Name:
Protein artemis, DNA cross-link repair 1C protein, Protein A-SCID, SNM1 homolog C, hSNM1C, SNM1-like protein, DCLRE1C, ARTEMIS, ASCID, SCIDA, SNM1C
Application Dilution: WB: 1:500~1:1000, IHC: 1:50~1:200
Specificity: p-Artemis (S516) polyclonal antibody detects endogenous levels of Protein artemis only when phosphorylated at Ser516.
Immunogen:
Synthetic phosphopeptide derived from human Artemis around the phosphorylation site of Serine 516.
MW: ~ 78 kDa
Swis Prot.: Q96SD1
Purification & Purity:
The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen and the purity is > 95% (by SDS-PAGE).
Format:
1mg/ml in PBS with 0.1% Sodium Azide, 50% Glycerol.
Storage:
Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles.
For research use only, not for use in diagnostic procedure.
Distinct DNA repair pathways minimize the consequences of mutagenic events. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are highly reactive atoms with an unpaired electron that are conducive to double-strand DNA breaking events. Artemis, named after the Greek goddess for the protection of children, is one of the major proteins contributing to the preservation of double-strand breaks in DNA by cutting away the damaged parts of the DNA, which allows the strands to rejoin. Artemis is a single-strand-specific 5' to 3' exonuclease that forms a complex with the 469 kDa DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PKcs). DNA-PKcs phosphorylates Artemis, and Artemis acquires endonucleolytic activity on 5' and 3' overhangs and hairpins. These activities are essential for V(D)J recombination and for the 5' and 3' overhang processing in nonhomologous DNA end joining.
Alternative Name:
Protein artemis, DNA cross-link repair 1C protein, Protein A-SCID, SNM1 homolog C, hSNM1C, SNM1-like protein, DCLRE1C, ARTEMIS, ASCID, SCIDA, SNM1C
Application Dilution: WB: 1:500~1:1000, IHC: 1:50~1:200
Specificity: p-Artemis (S516) polyclonal antibody detects endogenous levels of Protein artemis only when phosphorylated at Ser516.
Immunogen:
Synthetic phosphopeptide derived from human Artemis around the phosphorylation site of Serine 516.
MW: ~ 78 kDa
Swis Prot.: Q96SD1
Purification & Purity:
The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen and the purity is > 95% (by SDS-PAGE).
Format:
1mg/ml in PBS with 0.1% Sodium Azide, 50% Glycerol.
Storage:
Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles.
For research use only, not for use in diagnostic procedure.
| Is Featured? | No |
|---|
Write Your Own Review