ATP6V1B1 polyclonal, anti-human, mouse, rat
€305.00
In stock
SKU
BS5976
Background:
Vacuolar-type H+-ATPase (V-ATPase) is a multisubunit enzyme responsible for acidification of eukaryotic intracellular organelles. V-ATPases pump protons against an electrochemical gradient, while F-ATPases reverse the process, thereby synthesizing ATP. A peripheral V1 domain, which is responsible for ATP hydrolysis, and a integral V0 domain, which is responsible for proton translocation, compose V-ATPase. Nine subunits (A–H) make up the V1 domain and five subunits (a, d, c, c' and c") make up the V0 domain. Like F-ATPase, V-ATPase most likely operates through a rotary mechanism. The V-ATPase V1 B subunit exists as two isoforms. In the inner ear, the V-ATPase B1 isoform functions in proton secretion and is required to maintain proper endolymph pH and normal auditory function. The gene encoding the human V-ATPase B1 isoform maps to chromosome 2cen-q13. Mutations in this gene cause distal renal tubular acidosis associated with sensorineural deafness. The V-ATPase B2 isoform is expressed in kidney and is the only B isoform expressed in osteoclasts.
Alternative Name:
V-type proton ATPase subunit B, kidney isoform, V-ATPase subunit B 1, Endomembrane proton pump 58 kDa subunit, Vacuolar proton pump subunit B 1,ATP6B1, VATB, VPP3, V-ATPase B1
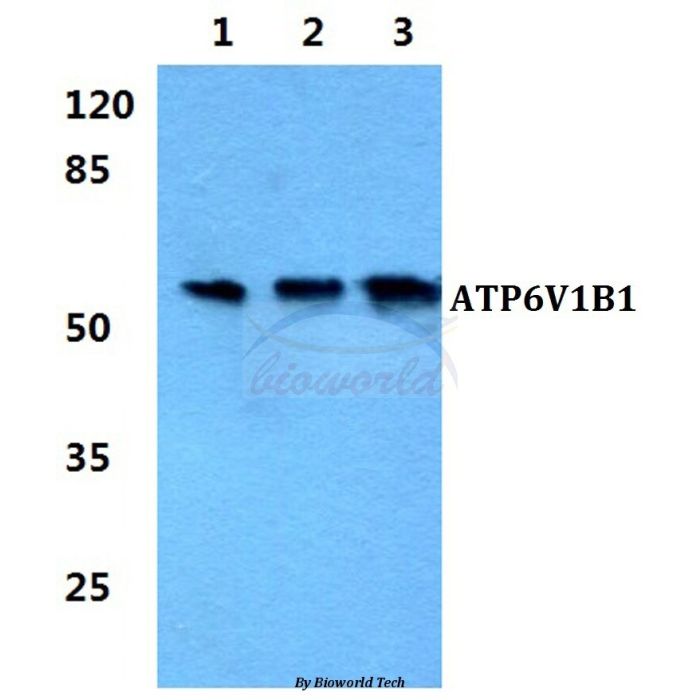
Application Dilution: WB: 1:500~1:1000, IHC: 1:50~1:200
Specificity: ATP6V1B1 polyclonal antibody detects endogenous levels of ATP6V1B1 protein.
Immunogen:
Synthetic peptide, corresponding to amino acids 426-471 of Human ATP6V1B1.
MW: ~ 58 kDa
Swis Prot.: P15313
Purification & Purity:
The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen and the purity is > 95% (by SDS-PAGE).
Format:
1 mg/ml in Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) with 0.05% sodium azide, approx. pH 7.2.
Storage:
Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles.
For research use only, not for use in diagnostic procedure.
Vacuolar-type H+-ATPase (V-ATPase) is a multisubunit enzyme responsible for acidification of eukaryotic intracellular organelles. V-ATPases pump protons against an electrochemical gradient, while F-ATPases reverse the process, thereby synthesizing ATP. A peripheral V1 domain, which is responsible for ATP hydrolysis, and a integral V0 domain, which is responsible for proton translocation, compose V-ATPase. Nine subunits (A–H) make up the V1 domain and five subunits (a, d, c, c' and c") make up the V0 domain. Like F-ATPase, V-ATPase most likely operates through a rotary mechanism. The V-ATPase V1 B subunit exists as two isoforms. In the inner ear, the V-ATPase B1 isoform functions in proton secretion and is required to maintain proper endolymph pH and normal auditory function. The gene encoding the human V-ATPase B1 isoform maps to chromosome 2cen-q13. Mutations in this gene cause distal renal tubular acidosis associated with sensorineural deafness. The V-ATPase B2 isoform is expressed in kidney and is the only B isoform expressed in osteoclasts.
Alternative Name:
V-type proton ATPase subunit B, kidney isoform, V-ATPase subunit B 1, Endomembrane proton pump 58 kDa subunit, Vacuolar proton pump subunit B 1,ATP6B1, VATB, VPP3, V-ATPase B1
Application Dilution: WB: 1:500~1:1000, IHC: 1:50~1:200
Specificity: ATP6V1B1 polyclonal antibody detects endogenous levels of ATP6V1B1 protein.
Immunogen:
Synthetic peptide, corresponding to amino acids 426-471 of Human ATP6V1B1.
MW: ~ 58 kDa
Swis Prot.: P15313
Purification & Purity:
The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen and the purity is > 95% (by SDS-PAGE).
Format:
1 mg/ml in Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) with 0.05% sodium azide, approx. pH 7.2.
Storage:
Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles.
For research use only, not for use in diagnostic procedure.
| Is Featured? | No |
|---|
Write Your Own Review