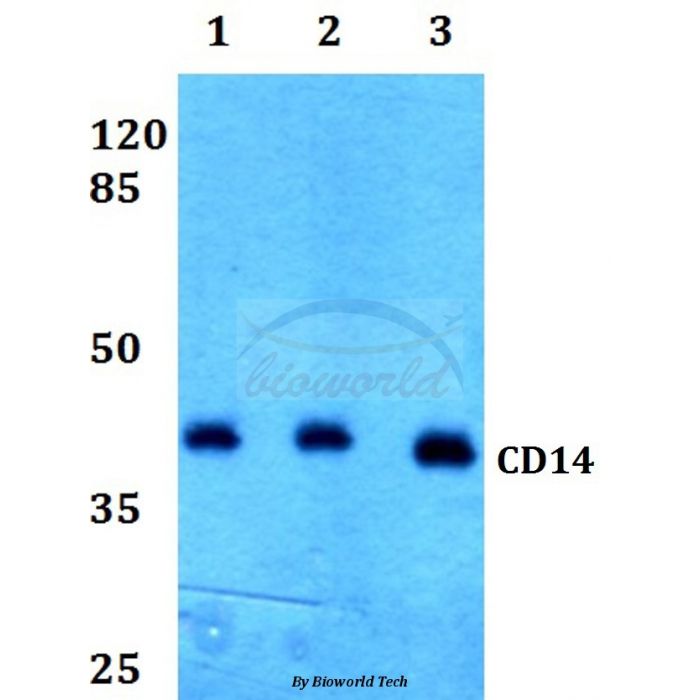
CD14 polyclonal, anti-human, mouse, rat
€305.00
In stock
SKU
BS60355
Background:
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) elicits the secretion of mediators and cytokines produced by activated macrophages and monocytes. CD14 is a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored protein found on the surfaces of monocytes and polymorphonuclear leukocytes. CD14 functions as a receptor for LPS, resulting in the secretion of various proteins. An important component in the LPS activation of monocytes through the CD14 receptor is the “adapter molecule,” lipopolysaccharide binding protein (LBP). There are two forms of CD14, a membrane-associated form (mCD14), and a soluble form (sCD14). mCD14 responds to LPS alone and facilitates the secretion of proteins, while cells not expressing mCD14 fail to respond to LPS. The cells that lack mCD14 respond to LPS/LBP in the presence of sCD14.
Alternative Name:
Monocyte differentiation antigen CD14, Myeloid cell-specific leucine-rich glycoprotein,CD_antigen=CD14, Cleaved into the following 2 chains: Monocyte differentiation antigen CD14, urinary form , Monocyte differentiation antigen CD14, membrane-bound form , CD14
Application Dilution: WB: 1:500~1:1000
Specificity: CD14 polyclonal antibody detects endogenous levels of CD14 protein.
Immunogen:
A synthetic peptide corresponding to residues in Human CD14.
MW: ~ 70 kDa
Swis Prot.: P08571
Purification & Purity:
The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen and the purity is > 95% (by SDS-PAGE).
Format:
1 mg/ml in Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) with 0.05% sodium azide, approx. pH 7.2.
Storage:
Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles.
For research use only, not for use in diagnostic procedure.
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) elicits the secretion of mediators and cytokines produced by activated macrophages and monocytes. CD14 is a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored protein found on the surfaces of monocytes and polymorphonuclear leukocytes. CD14 functions as a receptor for LPS, resulting in the secretion of various proteins. An important component in the LPS activation of monocytes through the CD14 receptor is the “adapter molecule,” lipopolysaccharide binding protein (LBP). There are two forms of CD14, a membrane-associated form (mCD14), and a soluble form (sCD14). mCD14 responds to LPS alone and facilitates the secretion of proteins, while cells not expressing mCD14 fail to respond to LPS. The cells that lack mCD14 respond to LPS/LBP in the presence of sCD14.
Alternative Name:
Monocyte differentiation antigen CD14, Myeloid cell-specific leucine-rich glycoprotein,CD_antigen=CD14, Cleaved into the following 2 chains: Monocyte differentiation antigen CD14, urinary form , Monocyte differentiation antigen CD14, membrane-bound form , CD14
Application Dilution: WB: 1:500~1:1000
Specificity: CD14 polyclonal antibody detects endogenous levels of CD14 protein.
Immunogen:
A synthetic peptide corresponding to residues in Human CD14.
MW: ~ 70 kDa
Swis Prot.: P08571
Purification & Purity:
The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen and the purity is > 95% (by SDS-PAGE).
Format:
1 mg/ml in Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) with 0.05% sodium azide, approx. pH 7.2.
Storage:
Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles.
For research use only, not for use in diagnostic procedure.
| Is Featured? | No |
|---|
Write Your Own Review