CD105 (Endoglin) polyclonal, anti-human, mouse
€305.00
In stock
SKU
BS60010
Background:
Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT) is an autosomal dominant disorder characterized by vascular abnormalities such as dilated vessels, hemorrhages, liver and lung congestion, and brain or heart ischemia. Mutations in two genes, Endoglin (also designated CD105) and ALK-1 (Activin receptorlike kinase 1, also designated TGFβ superfamily RI), are responsible for HHT. Endoglin is mutated in HHT1, and ALK-1 is mutated in HHT2, both of which are thought to be caused by haploinsufficiency. Endoglin and ALK-1 are type III and type I members of the TGFβ receptor superfamily, respectively, that are expressed on vascular endothelial cells. Endoglin can only bind ligands of the TGFβ superfamily via association with the respective ligand binding receptors for TGFβ1, TGFβ3, Activin-A, BMP-2 and BMP-7. The human ALK-1 gene encodes two protein species which exist as a result of either glycosylation or alternative splicing events. ALK-1 preferentially binds TGFβ1 and is expressed in bone marrow stromal cells, lung, brain, kidney and spleen.
Alternative Name:
Endoglin, CD105, ENG, END
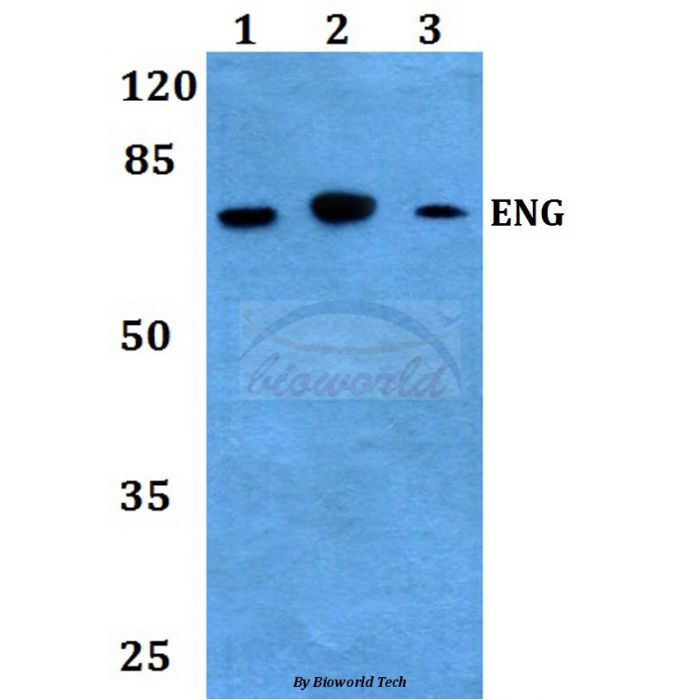
Application Dilution: WB: 1:500~1:1000
Specificity: Endoglin polyclonal antibody detects endogenous levels of Endoglin protein.
Immunogen:
A synthetic peptide corresponding to residues in Human Endoglin.
MW: ~ 70 kDa
Swis Prot.: P17813
Purification & Purity:
The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen and the purity is > 95% (by SDS-PAGE).
Format:
1mg/ml in PBS with 0.1% Sodium Azide, 50% Glycerol.
Storage:
Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles.
For research use only, not for use in diagnostic procedure.
Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT) is an autosomal dominant disorder characterized by vascular abnormalities such as dilated vessels, hemorrhages, liver and lung congestion, and brain or heart ischemia. Mutations in two genes, Endoglin (also designated CD105) and ALK-1 (Activin receptorlike kinase 1, also designated TGFβ superfamily RI), are responsible for HHT. Endoglin is mutated in HHT1, and ALK-1 is mutated in HHT2, both of which are thought to be caused by haploinsufficiency. Endoglin and ALK-1 are type III and type I members of the TGFβ receptor superfamily, respectively, that are expressed on vascular endothelial cells. Endoglin can only bind ligands of the TGFβ superfamily via association with the respective ligand binding receptors for TGFβ1, TGFβ3, Activin-A, BMP-2 and BMP-7. The human ALK-1 gene encodes two protein species which exist as a result of either glycosylation or alternative splicing events. ALK-1 preferentially binds TGFβ1 and is expressed in bone marrow stromal cells, lung, brain, kidney and spleen.
Alternative Name:
Endoglin, CD105, ENG, END
Application Dilution: WB: 1:500~1:1000
Specificity: Endoglin polyclonal antibody detects endogenous levels of Endoglin protein.
Immunogen:
A synthetic peptide corresponding to residues in Human Endoglin.
MW: ~ 70 kDa
Swis Prot.: P17813
Purification & Purity:
The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen and the purity is > 95% (by SDS-PAGE).
Format:
1mg/ml in PBS with 0.1% Sodium Azide, 50% Glycerol.
Storage:
Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles.
For research use only, not for use in diagnostic procedure.
| Is Featured? | No |
|---|
Write Your Own Review